What is Forex?
- Foreign Exchange (forex or FX) is simply the trading of one currency for another. It is the global marketplace for exchanging national currencies. For instance, one can swap the U.S. dollar for the Euro.
- Forex trading is the simultaneous act of buying one currency while selling another.
- The combination of these two currencies make up what's known as a currency pair. Currencies are always traded in pairs, and each currency in a pair is represented by a unique three-letter code.
- The first two letters in the code represent the country, and the third letter identifies the currency, such as the code JPY = Japanese Yen.
For example, a price or rate in euro-dollar could be quoted as:
EUR/USD = 1.23700
Major Currencies And The Seven Major Pairs:
| Major Currencies | Trading Symbol | Nickname | Major Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Euro | EUR | Anti-Dollar, Fiber | EUR/USD |
| British Pound | GBP | Sterling, Cable | GBP/USD |
| Australian Dollar | AUD | Aussie | AUD/USD |
| New Zealand Dollar | NZD | Kiwi | NZD/USD |
| US Dollar | USD | Greenback, Buck | |
| Canadian Dollar | CAD | Loonie | USD/CAD |
| Swiss Franc | CHF | Swissy | USD/CHF |
| Japanese Yen | JPY | Yen | USD/JPY |
How Are Currencies Traded?
- When an investor is speculating that the price will go up, he/she will buy the currency in order to sell it later at a higher price.
-
• When an investor is speculating that the price will go down, he/she will sell the currency in order to buy it later at a lower price.
Related terms:
Buy: Long, Bullish, Hawkish
Sell: Short, Bearish, Dovish
-
When you sell (go short) the EUR/USD:
(1) Selling the Euro
(2) Buying the US dollar
-
When you buy (go long) the EUR/USD:
(1) Buying the Euro
(2) Selling the US dollar
USD/EUR
Counter Currency
The counter currency is the second currency in the pair. Also known as variable currency or quote currency.
Base Currency
You “buy” or “sell” the base currency.
Points Vs. Pips Vs. Ticks

- Point, Pip, and Tick are price measurements used by speculators (traders) to describe price changes in the financial markets.
- A point is the largest price change of the three measurements. It represents the smallest possible price change on the left side of a decimal point.
- A pip, short for "point in percentage,“ represents the smallest change to the right of the decimal.
- A tick represents the smallest possible price change on the right side of a decimal point.
-
If price of EUR/USD increased from 1.19600 to 1.19610, by how many PIPs did the price increase?
1.19610-1.19600= 0.0001 1 PIP. -
If price of EUR/USD increased from 1.19600 to 1.19610, by how many PIPs did the price increase?
1.19610-1.19600= 0.0001 1 PIP. -
If price of EUR/USD increased from 1.18700 to 1.18800, by how many PIPs did the price increase?
1.18800-1.18700= 0.001 10 PIPs. -
If price of EUR/USD increased from 1.18700 to 1.18800, by how many PIPs did the price increase?
1.18800-1.18700= 0.001 10 PIPs. -
If price of EUR/USD increased from 1.18701 to 1.18700, by how many ticks did the price decrease?
1.18701-1.18700= 0.00001 1 Tick. -
We quote currency pairs by "5, 3 and 2" decimal places.
On a 5 decimal place currency pair a pip is 0.00010
On a 3 decimal place currency pair a pip is 0.010
On a 2 decimal place currency pair a pip is 0.10
Contract Size And Calculations
- A contract size is a standardized amount that tells buyers and sellers exact quantities that are being bought or sold, based on the terms of the contract.
- The size of the contract varies depending on the commodity or instrument.
- Contract is also referred to as lot or standard lot.
- 1 standard lot = 100,000 base currency
-
If you are buying or selling 1 contract of EUR/USD, it means that you are buying or selling 100,000 of
the base currency 100,000 Euro
0.5 Contract = ? 50,000 BC
0.1 Contract = ? 10,000 BC (Mini Lot)
0.01 Contract= ? 1000 BC (Micro Lot)
-
If price of EUR/USD increased from 1.18000 to 1.18001
change of 1 Tick.
1 Tick Change
1 lot= $1
0.1 lot= $0.1
0.01 lot= $0.01
Bid, Ask, And Spread
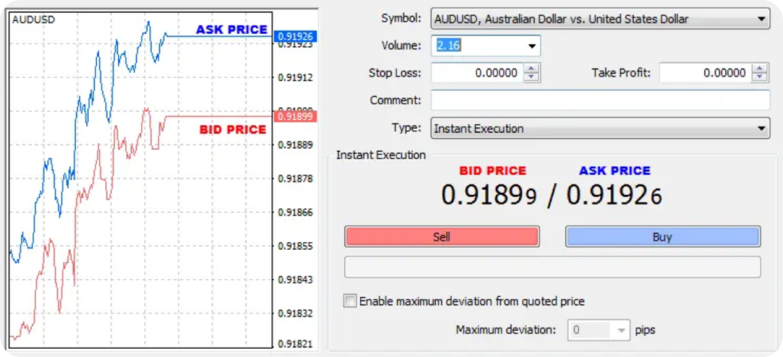
- The Bid Price is the price at which the investor is willing to sell the currency.
- The Ask Price, also known as offer, is the price at which the investor is willing to buy the currency.
-
The Spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices (0.091926 – 0.91899 = 0.00027)
The spread in the above case is 2.7 pips or 27 ticks. - 1 standard lot = 100,000 base currency

Profit And Loss Calculations
-
To calculate a long transaction’s profit or loss, the following formula is to be used:
(Closing price – Opening price) * Number of Contracts * Contract Size.
For example:
A trader bought 2 EUR/USD contracts at 1.20500 and sold them at 1.22000. Calculate the profit or loss.
Solution: (1.22000 – 1.20500) * 2* 100,000= USD 3,000
-
To calculate a short transaction’s profit or loss, the following formula is to be used:
(Opening price - Closing price) * Number of Contracts * Contract Size.
For example:
A trader sold 3 AUD/USD contracts at 0.77500 and bought them at 0.76000. Calculate the profit or loss.
Solution: (0.77500 - 0.76000) *3*100,000= USD 4,500
-
Unrealized P/L:
Unrealized P/L refers to the profit or loss held in your current open positions….your currently active trades.
This is equal to the profit or loss that would be “realized” if all your open positions were closed immediately.
Unrealized P/L is also known as “Floating P/L” because the value is constantly changing since your positions are still open.
- Balance: Balance is the amount available without taking into consideration the unearned/floating profit and loss.
- Equity: Equity is the available net balance. It is equal to balance ± profit or loss.
| 5095.00 USD | |
|---|---|
| Balance | EUR/USD |
| Equity | GBP/USD |
| Margin | AUD/USD |
| Free Margin | NZD/USD |
| US Margin Level (%) | |
|
Positions
US30Z0 - buy 1
30009.00
30251.50
|
2 425.00 |
|
US30Z0 - buy 1
29984.50
30251.50
|
2 670.00 |
Margin And Leverage
-
What is Margin?
When trading forex, you are only required to put up a small amount of capital to open and maintain a new position.
This capital is known as the margin. -
What is Leverage?
Leverage is the use of various financial instruments on borrowed capital, to increase the potential return of an investment.
Further, it may also increase your risk exposure. -
When margin is expressed as a specific amount of your account’s currency, this amount is known as the Required Margin.
Each position you open will have its own Required Margin amount that will need to be “locked up”.
Required Margin is also known as Deposit Margin, Entry Margin, or Initial Margin. Let’s look at a typical EUR/USD (euro against U.S. dollar) trade. To buy or sell a 100,000 of EUR/USD without leverage would require the trader to put up $100,000 in account funds, the full value of the position.
But with a Margin Requirement of 2%, only $2,000 (the “Required Margin“) of the trader’s funds would be required to open and maintain that $100,000 EUR/USD position. If you add up all of the Required Margin of all the positions that are open, the total amount is what’s called the Used Margin.
Now, Free margin is the amount available to use, to enter new trades. Free margin = Equity – Used Margin -
What is the Margin Level ?
Margin Level allows you to know how much of your funds are available for new trades. Margin Level = (Equity/ Used Margin) * 100%
The higher the Margin Level, the more Free Margin you have available to trade., and the lower the Margin Level, the less Free Margin available to trade.
Which could result a Margin Call or a Stop Out. When margin level reaches 100%, it means your equity is equal to your used margin; which is called “margin call”.
When margin level reaches 20%, this is called “stop out level”. If this level is reached, your broker will automatically start closing out your trades starting with the most unprofitable one until your Margin Level is back above the Stop Out Level.
Market Order And Pending Orders:
-
Market Order (Market Execution):
•Order to buy or sell an instrument at the current market price, directly whatever the fill will be. You get the price available directly. -
Take Profit:
Automatically closes a position when the asset's price reaches a predetermined level, allowing a trader to lock in profits at that point. -
Stop Loss:
Automatically closes a position when the asset's price reaches a specified level, helping traders limit potential losses by exiting the trade at a predetermined point. -
Pending Orders (Limit Orders):
Limit orders provide the trader with an opportunity to buy or sell a currency pair at a specific price above or below the current market price.
-Buy Limit order
- Sell Limit order
- Buy Stop order
-Sell Stop order - A buy limit is a pending order in trading that instructs a broker to buy an instrument at a price lower than the current market price when that price level is reached, often used to enter a trade at a more favorable price point.
- A sell limit is a pending order in trading that instructs a broker to sell an instrument at a price higher than the current market price when that price level is reached, often used to initiate a trade at a more favorable price point.
- A buy stop is a pending order that instructs a broker to buy an instrument at a price higher than the current market price when that price level is reached, often used to enter a trade as the price rises and potentially continues an upward trend.
- A sell stop is a pending order that instructs a broker to sell an instrument at a price lower than the current market price when that price level is reached, often used to initiate a trade as the price declines and potentially continues a downward trend.